The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) has revolutionised the industrial landscape, creating a seamless web of interconnected devices. Imagine a mining operation where every machine communicates in real-time, optimising processes and maximising efficiency. This article delves into what is IIoT, its components, and its transformative impact on industrial automation.
8 min read
What is IIoT?
“IIoT is an extension of IoT into industrial settings, seamlessly integrating smart technologies into traditional industries. While IoT encompasses a wide range of applications, IIoT specifically focuses on enhancing efficiency, predictive maintenance, and data-driven decision-making in industrial processes.”
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is transforming how industrial operations are monitored, controlled, and optimised. By connecting sensors, devices, and control systems to the cloud, IIoT enables real-time data collection and advanced analytics that drive smarter decision-making and improved performance.
In mining and mineral processing, IIoT is a cornerstone of digital transformation—helping operations become safer, more efficient, and more sustainable.
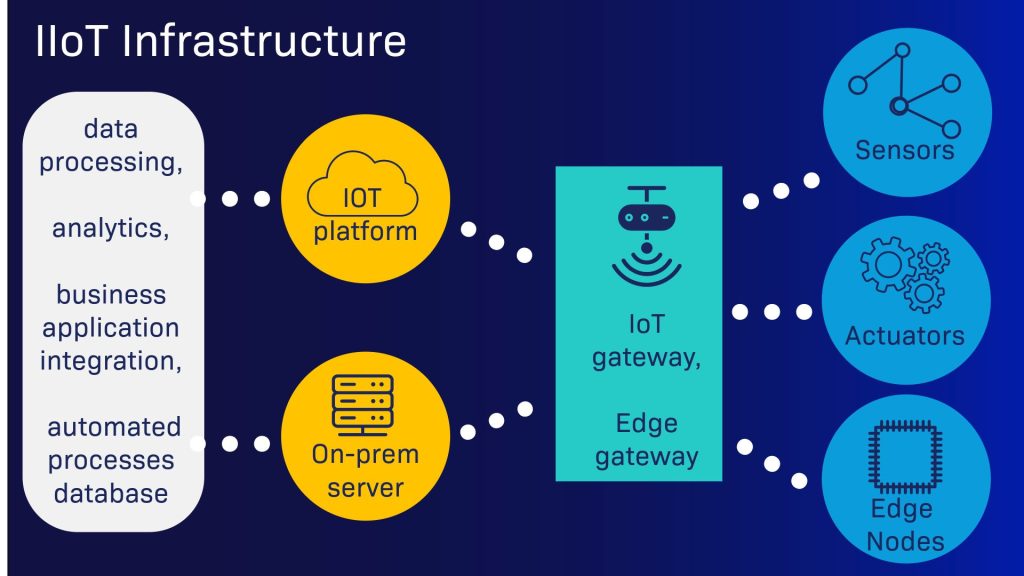
Why IIoT matters in Industrial Automation
IIoT extends traditional automation by integrating smart devices, edge computing, and cloud-based analytics. This connectivity allows operators to:
- Monitor equipment health in real time
- Predict failures before they occur
- Optimise energy use and throughput
- Reduce manual intervention and downtime
For plant managers, IIoT means greater visibility across the entire operation, from crushers and mills to flotation cells and smelters.
Key elements of IIoT: sensors, actuators and interconnected devices
An effective IIoT ecosystem includes:
- Smart sensors: Capture data on temperature, vibration, pressure, and flow
- Edge devices: Process data locally for faster insights
- Cloud platforms: Store and analyse data at scale
- Connectivity protocols: Ensure secure and reliable communication
- AI and machine learning: Turn raw data into actionable insights
At the heart of IIoT lies the interplay between sensors and actuators. These devices serve as organs within the realm by collecting data from various sources and transmitting it for analysis and action.
Sensors play a role in detecting environmental changes such as temperature, pressure or vibration. On the other hand, actuators are responsible for translating commands into physical actions. By doing machines can effectively respond to the insights derived from the collected data.
The connectivity aspect of IIoT is equally important as it serves as the foundation for an interconnected network. When we explore communication protocols, we discover the ways devices interact with each other. This ensures that data flows reliably and robustly throughout the network. The intricate dance between devices, facilitated by these protocols, sets the stage for the interconnected intelligence that defines IIoT.
Innovations like edge computing are revolutionising IIoT by going beyond data processing methods. Processing data at the edge – closer to where it’s generated. It plays a role in accelerating decision-making processes while minimising delays and enhancing overall system agility. The edge becomes a point where data and action converge, ushering in an era of heightened responsiveness.
One crucial aspect to understand when navigating through IIoT is its integration with existing industrial automation systems. The synergy between IIoT and automation goes beyond integration; it represents a paradigm shift in how industries operate.
Connected operations: Realising efficiency gains through IIoT and Automation
In the realm of industry, the marriage of the IIoT with automation technologies has ushered in an era of unprecedented connectivity and intelligence.
To truly understand the impact of IIoT, let’s focus on industries, each with its unique challenges and opportunities. In the mining industry, IIoT proves to be a tool for optimising operations and ensuring safety.
IIoT in action: mining use cases
At Mipac, we’ve seen IIoT deliver measurable results across multiple mining sites:
- Predictive maintenance: Using vibration and temperature data to prevent motor failures
- Process optimisation: Real-time feedback loops that adjust reagent dosing or airflow
- Remote monitoring: Enabling centralised control rooms to oversee multiple sites
- Energy efficiency: Identifying energy-intensive assets and optimising load distribution
Data analytics and machine learning
IIoT significance goes beyond data collection and connectivity; it intersects with the power of data analytics. Raw data holds potential. With IIoTs’ network of sensors and connectivity, industries can extract insights through advanced data analytics.
In the context of IIoT, data analytics becomes the key to unlocking intelligence. By analysing patterns, trends and anomalies in amounts of data, industries understand their operations. This empowers decision-makers to make choices that drive efficiency and optimise processes.
However, the true pinnacle of IIoTs’ potential is reached when incorporating machine learning algorithms.
These advanced algorithms go beyond programming, allowing systems to learn and adapt based on patterns in data. In the automation field, machine learning plays a role in predictive maintenance.
Predictive maintenance made possible through IIoT and machine learning represents a shift from reactive to approaches. Waiting for a machine to break down, IIoT predicts issues by analysing data trends, enabling timely interventions. This does not reduce downtime. It also extends the lifespan of equipment, resulting in substantial cost savings for industries.
Ensuring security in the realm of IIoT
As we delve deeper into the interconnected web of IIoT, it becomes vital to address the challenges posed by securing these interconnected devices. The very nature of IIoT, where devices communicate and share data seamlessly, creates vulnerabilities.
Securing IIoT systems goes beyond cybersecurity measures as it requires understanding the complexities involved in interconnected devices and their potential weak points. Challenges arise not only from threats but also from managing a vast network of devices with their own specific security considerations.
When navigating the security landscape of IIoT, it is crucial to explore strategies and technologies specifically designed to safeguard the integrity of these interconnected systems.
Encryption, authentication and strong access controls serve as the line of defence. In addition to these measures, anomaly detection systems play a role in identifying behaviour patterns that may indicate a security breach.
Furthermore, the concept of security in the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) extends throughout the lifecycle of devices from their manufacturing to their decommissioning. Secure boot processes, over-the-air updates with verification and secure device provisioning, are components in strengthening the defences of IIoT systems.
Benefits of IIoT in Industrial Automation
- Increased uptime through predictive analytics
- Improved safety with remote diagnostics and alerts
- Lower operating costs via automation and optimisation
- Scalability across multiple plants and assets
- Enhanced ESG compliance through data transparency
IIoT is not just an upgrade but a catalyst for efficiency gains, cost savings, and operational excellence.
One significant benefit of IIoT lies in its ability to enhance efficiency. Through real-world examples, we can observe how IIoT optimises production processes, reduces downtime, and streamlines workflows. The interconnected intelligence provided by IIoT enables coordination and responsiveness at previously unimaginable levels.
Cost savings naturally arise from the impact of IIoT on operations. Predictive maintenance made possible by combining IIoT with machine learning not only reduces costs associated with equipment failures but also extends machinery lifespan. Using data to make informed decisions plays a role in allocating resources, leading to cost savings.
Challenges and considerations
Like any shift, IIoT presents its own set of challenges and considerations. However, these obstacles are not insurmountable. Recognising and understanding these challenges is vital for industries looking to leverage the potential of IIoT.
Bandwidth Limitations
In a network of devices, bandwidth limitations can become a bottleneck. The sheer amount of data generated by sensors and devices requires high-speed networks. Overcoming limitations involves adopting an approach that optimises data transmission protocols and utilises advanced networking technologies.
Standardisation Issues
The IIoT ecosystem comprises devices, communication protocols and technologies necessitating industry standardisation. Without frameworks, achieving interoperability becomes challenging as it hampers the seamless integration of devices from different manufacturers. The importance of protocols and communication frameworks cannot be overstated for the adoption and success of IIoT.
Integration, with 5G
The arrival of 5G technology marks an era for IIoT. The remarkable speed and minimal delay of 5G networks unlock the potential of IIoT by enabling real-time communication between devices. Incorporating 5G into IIoT ecosystems does not enhance data transmission capabilities. It also creates opportunities for applications that require immediate responsiveness, such as remotely controlling machinery and implementing augmented reality in industrial settings.
Rising Technologies
In addition to 5G, emerging technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) and blockchain promise to enhance the capabilities of IIoT. AI, with its ability to analyse data sets and make decisions, complements the data-driven nature of IIoT. Machine learning algorithms, crucial in IIoT applications, will become more advanced, empowering systems to adapt and evolve instantaneously.
Blockchain technology, renowned for its transparent ledger system, addresses the security concerns in IIoT. By providing a record of transactions and data exchanges, blockchain strengthens the integrity of IIoT systems.
Moreover, it also enables the management of supply chains in a transparent manner, which is extremely important in industries where traceability and accountability hold great significance.
Effectively addressing these challenges requires collaboration among industry stakeholders, policymakers and technology developers. Industry consortia and standardisation bodies play a role in establishing frameworks that ensure compatibility and interoperability across diverse IIoT ecosystems.
The future of IIoT is not set in stone; it’s an evolving journey that continues to unfold. As we look ahead, specific trends emerge, shaping the chapters of IIoT’s story.
Unleash the power of Mining 4.0 with Mipac
The future of industrial technology is here, and Mipac is your trusted partner in navigating this exciting frontier. Embrace the possibilities, join the conversation, and let Mipac guide you on a transformative journey towards a more connected and efficient industrial future.
With our wealth of expertise and experience in all areas of Mining 4.0, we can help guide your journey towards safer, more efficient, and sustainable mining operations.
We consult on topics including:
- Control philosophy development
- Digital maturity assessments
- Digital transformation roadmaps
- Change leadership in OT
- Advanced Process Control (APC)
- And ESG monitoring and reporting
Contact us today to explore how we can collaborate to drive innovation and success in your mining endeavours.
Explore our insights into digital transformation and Mining 4.0
Generative vs predictive AI in mineral processing plants
AI in mineral processing is no longer a future concept - it’s happening now. From…
What is IIoT in Industrial Automation? A Comprehensive Overview
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) has revolutionised the industrial landscape, creating a seamless web…
What Is Industrial Automation? 2025 guide to efficiency, AI & smart operations
In this article, we explore what is industrial automation, the benefits it delivers and how…
Some of your top FAQs on this topic
IoT typically refers to consumer devices (like smart homes), while IIoT is designed for industrial environments with higher reliability, security, and scalability requirements.
Security in remote locations is crucial. IIoT fortifies industrial operations by employing encryption and authentication protocols. Continuous monitoring is a vigilant guardian, detecting and mitigating potential cybersecurity threats. These measures ensure uninterrupted orchestration, even in the challenging landscapes of remote mining sites.
Absolutely! IIoT transforms the utilities sector by orchestrating smart grids. These grids act as virtuoso conductors, optimising the distribution of energy. Real-time data allows for adaptive adjustments, reducing waste and cutting costs. The result is a harmonious distribution of power that aligns with the community's dynamic needs.
Addressing bandwidth limitations in water/utilities settings involves strategic solutions. IIoT systems navigate these challenges by implementing local data storage and optimising communication protocols. This strategic overture ensures a consistent flow of data, overcoming bandwidth limitations in remote locations.
The future of IIoT promises exciting trends that will reshape industries. Integrating 5G technology will enable faster data transmission, which is particularly beneficial in dynamic environments like mining. Emerging technologies like AI algorithms and blockchain will take centre stage, enhancing data analysis and ensuring secure and transparent data transactions. These trends herald a new era of connectivity, efficiency, and innovation in the industrial landscape.



